Solar Power Solutions

Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV),
indirectly using concentrated solar power, or a combination. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors
and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an
electric current using the photovoltaic effect.
DRS is a market leader with expertise in end-to-end energy management systems and solutions including Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution and Power Storage.
DRS will contribute to the development of Power sector with its experience, expertise and technology innovation
0.5 Kilowatt System
| S.No | Appliances | Watts | Nos | Backup Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CFL | 15W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 2 | TUBE LIGHT | 40W | 1 | 6hrs |
| 3 | FAN | 60W | 1 | 6hrs |
| 4 | LCD TV | 90W | 1 | 5hrs |
1 Kilowatt System
| S.No | Appliances | Watts | Nos | Backup Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CFL | 15W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 2 | TUBE LIGHT | 40W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 3 | FAN | 60W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 4 | LCD TV | 90W | 1 | 5hrs |
| 5 | PC | 140W | 1 | 5hrs |
1.5 Kilowatt System
| S.No | Appliances | Watts | Nos | Backup Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CFL | 15W | 4 | 6hrs |
| 2 | TUBE LIGHT | 40W | 3 | 6hrs |
| 3 | FAN | 60W | 3 | 6hrs |
| 4 | LCD TV | 90W | 1 | 6hrs |
| 5 | PC | 140W | 1 | 6hrs |
2 Kilowatt System
| S.No | Appliances | Watts | Nos | Backup Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CFL | 15W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 2 | TUBE LIGHT | 40W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 3 | FAN | 60W | 2 | 6hrs |
| 4 | LCD TV | 90W | 1 | 5hrs |
| 5 | PC | 140W | 1 | 4hrs |
| 6 | REFRIGERATOR | 400W | 1 | 4hrs |
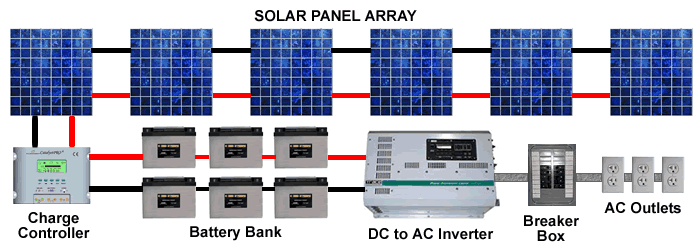
To use the energy from the array, you may also need other components, such as inverters, charge controllers and batteries, which make up a solar-electric system. The components required are dependent on the system type designed. System types include:

PV-DIRECT SYSTEMS:
These are the simplest of solar-electric systems, with the fewest components (basically the PV array and the load). Because they don’t have batteries and are not hooked up to the utility, they only power the loads when the sun is shining. This means that they are only appropriate for a few select applications, notably water pumping and ventilation—when the sun shines, the fan or pump runs.
OFF-GRID SYSTEMS:
Although they are most common in remote locations without utility service, off-grid solar-electric systems can work anywhere. These systems operate independently from the grid to provide all of a household’s electricity. These systems require a battery bank to store the solar electricity for use during nighttime or cloudy weather, a charge controller to protect the battery bank from overcharge, an inverter to convert the DC PV array power to AC for use with AC household appliances, and all the required disconnects, monitoring, and associated electrical safety gear.
GRID-TIED SYSTEMS WITH BATTERY BACKUP:
This type is very similar to an off-grid system in design and components, but adds the utility grid, which reduces the need for the system to provide all the energy all the time.
BATTERYLESS GRID-TIED SYSTEMS:
These most common PV systems are also known as on-grid, grid-tied, utility-interactive, grid-intertied, or grid-direct. They generate solar electricity and route it to the loads and to the electric utility grid, offsetting a home’s or business’s electricity usage. System components are simply comprised of the PV array, inverter(s), and required electrical safety gear (i.e., fuses/breakers/disconnects/monitoring). Living with a grid-connected solar-electric system is no different than living with utility electricity, except that some or all of the electricity you use comes from the sun. (The drawback of these batteryless systems is that they provide no outage protection—when the utility grid fails, these systems cannot operate.)